Lead Acid Battery - what is it?
Lead-acid battery
Lead-acid battery is the secondary power source (rechargeable battery)
with lead electrodes and sulfuric acid electrolyte. It is used to store electric energy, generated by some
primary power source (generator or, in the past, the primary battery).
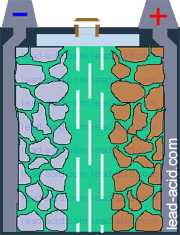
Main parts of lead acid battery are:
- battery case (jar, that contains other parts of the battery);
- battery cover, that prevents electrolyte splashing;
- positive plate that consists of lead grid and active mass of oxidized lead (PbO2);
- negative plate with lead grid and lead active mass;
- electrolyte (water + sulfuric acid) surrounding plates;
- separator (plastic or glass mat) preventing plate contact;
- terminals for connecting wires to lead-acid battery.
Lead-Acid battery - how does it work
In order to store electric energy inside lead-acid battery
it needs to be charged. During the charging, electric current produced by some external power source flows
to lead-acid battery and causes chemical reactions in it.
The simplified chemical reaction for lead-acid battery in whole
during battery charging can be described as:
PbSO4(+) + PbSO4(-) + 2H2O -> PbO2(+) + Pb(-) + 2H2SO4
During this reaction lead sulfate (PbSO4) of the positive
plate (electrode) is converted to oxidized lead (PbO2) while the same substance on the negative
plate is converted to lead (Pb). Sulfur from both plates goes to the electrolyte thus increasing the acid
concentration. The total energy in the right part of the equation is larger than the energy in the left part
of the equation and the energy difference is stored in lead-acid battery.
Charged lead-acid battery is stable for months or even years and electric
energy saved in it could be released at any time. To release energy one needs to connect lead-acid battery
terminals to some load. This process is called battery discharge. During discharge the simplified chemical
reaction mentioned above is reversed:
PbO2(+) + Pb(-) + 2H2SO4 -> PbSO4(+) + PbSO4(-) + 2H2O

Lead-acid battery load
Lead-acid battery active materials (Pb and PbO2) from both
plates are converted to lead sulfate (PbSO4) while acid concentration and electrolyte density
decrease.
During battery discharge electric energy stored in the battery
produces some work in an external load: lamp is lit, golf cart goes to a hole, car engine starts and so on.
Lead-Acid battery - History and Variety
Lead acid battery was the first known type of rechargeable battery.
It was suggested by French physicist Gaston Planté in 1860 (Comptes, rendus, t. L, p. 640. Mars 1860).
A lot of good things happened to lead-acid batteries from that time.
Lead-acids have now more capacity, provide larger currents, are more compact and much, much cheaper.
Modern lead-acid batteries are used in many areas with some specific
battery construction for every application. Lead-acid batteries can be grouped (or devided) in many different
ways.
Some lead-acid battery groups (sometimes intersecting) are:
- Car (starter) batteries;
- Industrial batteries;
- Traction batteries;
- UPS batteries;
- stationary batteries;
- UPS batteries;
- deep cycle batteries;
- front terminal batteries.
Technical characteristics of lead-acid batteries
Main technical characteristics of lead scid batteries are shortly
named below.
Number of cells. Lead-acid battery can consist of of one cell with
2 V nominal voltage or be composed of several 2-volt cells. The most common number of cells in lead-acid
batery is 6.
Battery voltage. Lead-acid battery voltage varties according to the
number of cells in a battery. Lead-acid battery can be 2-volt, 4-volt, 6-volt, 8-volt, 12-volt or 24 volt.
The most common battery voltage is 12 V. To achive larger voltages batteries are connected in series.
Battery capacity. The capacity of lead-acid battery can vary from
1 ampere-hour (Ah) to more than 5000 Ah. To achive larger battery capacity sometimes parallel connection
of lead-acid batteries is used. Batteries with large capacity usually have less cells (and less voltage)
to be more compact.
Battery energy capacity. Lead-acid battery power capacity can vary
from 10 Wh to more than 10 000 watts watt-hours.
Specific energy of lead-acid battery is far from battery records -
only about 30 Wh/kg.
Maximum discharge current - here is the raison d'etre for lead-acid
batteries - up to 1000 A could be taken from the largest batteries without any harm. Short cirquit
currents for lead-acids can reach fantastic 30 000 amps.
Battery price - is the second reason of existance of lead-acid
batteries. There are cheap. Cheaper than any other battery with the same energy capacity.
|